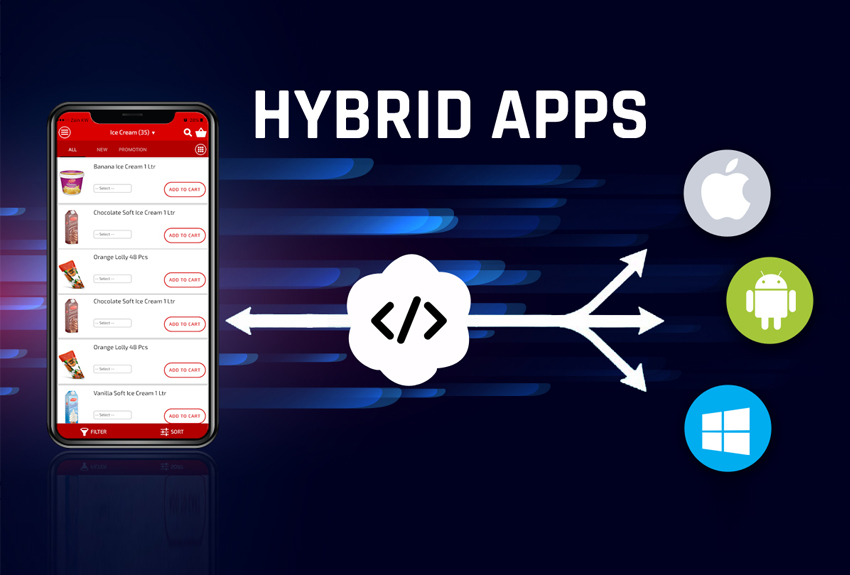
Cross-platform development refers to the creation of software applications which are compatible with multiple devices and operating systems (OS) by using a single codebase. This approach contrasts with native development, where separate codebases are written for each platform (e.g., iOS, Android, Windows).
Embracing cross-platform development can offer numerous advantages to businesses:
Cost Efficiency:
Reduced Development Costs: A single codebase means less time and fewer resources are needed compared to developing separate native applications for each platform.
Lower Maintenance Expenses: Updates and bug fixes are applied once and propagated across all platforms, saving on long-term maintenance costs.
Faster Time-to-Market:
Simultaneous Deployment: Businesses can launch their applications on multiple platforms at the same time, accelerating market entry.
Streamlined Development Process: Unified development reduces the complexity and duration of the project lifecycle.
Wider Audience Reach:
Increased User Base: By supporting multiple platforms (e.g., iOS, Android, web), businesses can access a broader audience.
Global Market Penetration: Cross-platform apps can cater to users in different regions who prefer different devices.
Consistent User Experience:
Uniform Design and Functionality: A single codebase ensures that the application’s look, feel, and performance are consistent across all platforms.
Brand Integrity: Consistency strengthens brand recognition and trust among users.

Simplified Maintenance and Updates:
Unified Updates: Changes are made once and reflected everywhere, simplifying version control.
Easier Bug Tracking: A single codebase makes it easier to identify and fix issues.
Resource Optimization:
Efficient Use of Development Teams: Developers can focus on one project rather than juggling multiple platform-specific projects.
Skill Utilization: Teams can leverage common programming languages and frameworks, maximizing their expertise.
Reusability of Code:
Modular Development: Components and modules can be reused across different parts of the application or even in future projects.
Improved Efficiency: Reusability reduces redundancy, leading to faster development cycles.
Simplified Testing and Quality Assurance:
Unified Testing Process: Testing efforts are centralized, reducing the time and resources needed for QA.
Consistent Performance Metrics: Easier to monitor and maintain performance standards across platforms.
Competitive Advantage:
Agility: Faster development and deployment allow businesses to respond quickly to market changes and customer feedback.
Innovation Focus: Savings in time and cost can be redirected toward innovative features and enhancements.
Future-Proofing:
Scalability: Cross-platform frameworks often support easy integration with new technologies and platforms.
Adaptability: Businesses can quickly adapt applications to emerging devices and operating systems without starting from scratch.
Enhanced Collaboration:
Cross-Functional Teams: Unified development fosters better collaboration among team members, improving overall project cohesion.
Shared Knowledge Base: Developers work within the same environment, facilitating knowledge sharing and problem-solving.
Better ROI:
Higher Revenue Potential: Broader market reach and faster deployment can lead to increased sales and revenue streams.
Optimized Investment: Lower development and maintenance costs improve the return on investment.
In Summary
Cross-platform development offers a strategic advantage for businesses looking to maximize their resources while delivering high-quality applications to a diverse user base. By reducing costs, speeding up development, and ensuring consistency across platforms, businesses can enhance their competitiveness and profitability in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Popular Cross-Platform Frameworks
React Native: Developed by Facebook, it allows for building mobile apps using JavaScript and React.
Flutter: Google’s UI toolkit for crafting natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase.
Considerations
While cross-platform development offers many benefits, it’s essential to consider factors like performance requirements, access to native device features, and the complexity of the user interface when choosing between cross-platform and native development. In some cases, a hybrid approach might be the most effective strategy.